Oct 2, 2023 | Outsourcing, Outsourcing Techniques
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations face increasing pressure to remain competitive, efficient, and adaptable. One way companies achieve this is by outsourcing non-core functions, and one of the most popular areas for outsourcing is Human Resources (HR). This comprehensive guide will take you through everything you need to know about outsourcing HR functions. We’ll explore the reasons behind this trend, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and the critical factors to consider when deciding if outsourcing HR is right for your organization.
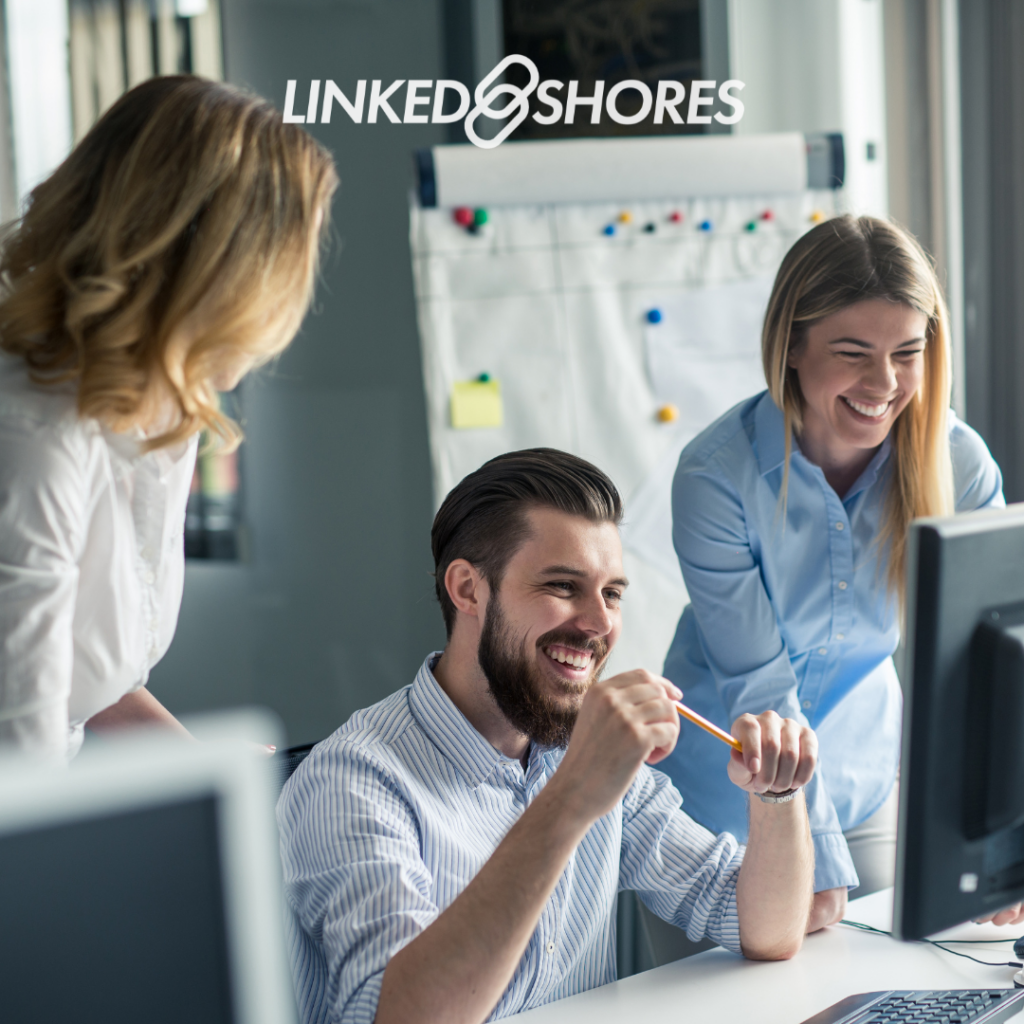

Understanding HR Outsourcing
In this chapter, we will delve deeper into the concept of HR outsourcing, providing a comprehensive understanding of what it entails, its historical context, and the types of HR functions typically outsourced. By the end of this chapter, you will have a solid foundation for exploring the world of HR outsourcing.
What is HR Outsourcing?
HR outsourcing, often referred to as Human Resources Outsourcing (HRO), is the practice of entrusting specific HR functions to external service providers. These providers are experts in HR management and administration, and they handle a range of tasks on behalf of organizations. The primary aim of HR outsourcing is to streamline HR processes, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and allow organizations to focus on their core business activities.
The Historical Context
To truly grasp the significance of HR outsourcing, it’s essential to understand its historical context. The evolution of HR outsourcing can be traced back to the late 20th century when businesses started recognizing the need for greater efficiency and cost savings. Here’s a brief historical overview:
1970s-1980s: The concept of outsourcing emerged as companies sought ways to reduce costs and enhance productivity. Initially, functions like manufacturing and IT were outsourced.
1990s: HR outsourcing gained traction as organizations began to realize the potential benefits of delegating HR tasks to specialized providers.
2000s-Present: The HR outsourcing industry has continued to grow and adapt to changing business needs. Today, it encompasses a wide range of services, from payroll processing to talent acquisition and employee benefits administration.
Common HR Functions Outsourced
HR outsourcing encompasses a diverse array of functions, each serving a specific purpose in the HR landscape. Here are some of the most commonly outsourced HR functions:
Payroll Processing: Outsourcing payroll tasks can reduce errors and ensure that employees are paid accurately and on time.
Recruitment and Staffing: Many companies partner with external firms to handle the recruitment process, from sourcing candidates to conducting interviews and background checks.
Benefits Administration: The management of employee benefits, such as health insurance, retirement plans, and leave policies, is often outsourced to ensure compliance and efficiency.
Compliance and Regulatory Reporting: Keeping up with ever-changing labor laws and regulations can be complex. Outsourcing this function helps organizations stay compliant.
Employee Training and Development: Some organizations outsource training programs and employee development initiatives to leverage specialized expertise.
HR Technology Solutions: Cloud-based HR software and technology solutions are often provided by external vendors, simplifying HR processes and data management.
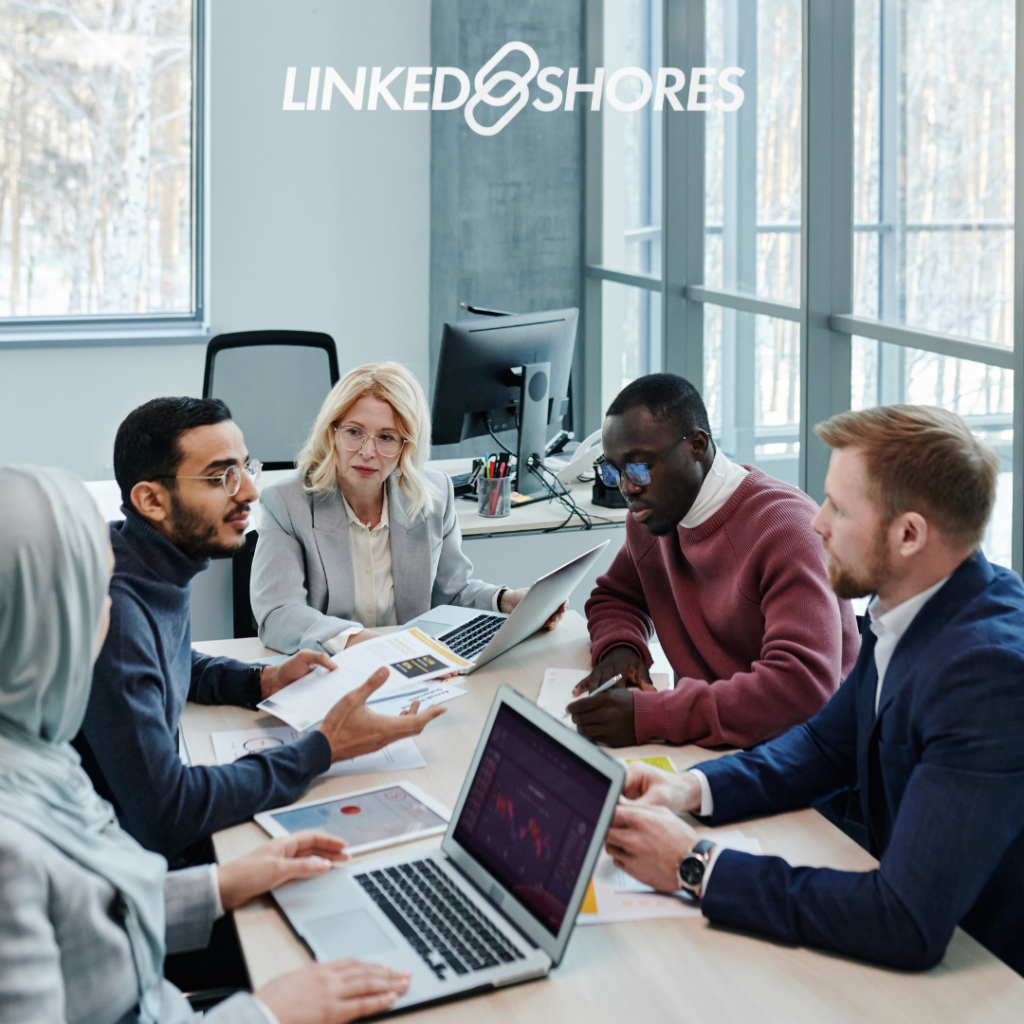

Advantages of Outsourcing HR Functions
Cost Savings
Detail how outsourcing HR functions can lead to cost savings through reduced overhead, access to specialized expertise, and minimized risks associated with non-compliance.
Focus on Core Competencies
Explain how outsourcing allows organizations to concentrate on their core business activities, leading to improved productivity and innovation.
Scalability and Flexibility
Highlight the flexibility HR outsourcing provides, enabling companies to scale their HR services up or down based on changing needs.
Expertise and Technology
Discuss the advantages of accessing cutting-edge technology and industry expertise through outsourcing partners.
Potential Drawbacks of HR Outsourcing
Loss of Control
Address concerns related to relinquishing control over HR processes and decision-making.
Data Security and Confidentiality
Discuss the importance of data security and confidentiality, emphasizing the need for robust contracts and safeguards.
Employee Morale and Communication
Examine how HR outsourcing can impact employee morale and communication within the organization.
Types of HR Outsourcing
Full-Service Outsourcing
Explain how full-service outsourcing involves delegating all HR functions to a third-party provider.
Partial Outsourcing
Detail partial outsourcing, where specific HR functions, such as payroll or recruitment, are outsourced while others remain in-house.
Cloud-Based HR Solutions
Introduce cloud-based HR solutions as a subset of outsourcing, emphasizing the benefits of flexibility and accessibility.
Future Trends in HR Outsourcing
In this forward-looking chapter, we’ll delve into the future of HR outsourcing, examining emerging trends and developments that are poised to shape the landscape of Human Resources Outsourcing (HRO) in the coming years. Staying ahead of these trends will be crucial for organizations seeking to optimize their HR operations and adapt to evolving workforce dynamics.
The Advent of Artificial Intelligence and Automation
AI-Driven HR: Explore how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing HR by automating routine tasks, such as resume screening and initial candidate interviews, allowing HR professionals to focus on strategic aspects of talent management.
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: Discuss the growing use of chatbots and virtual assistants in HR functions, including answering employee queries, providing onboarding support, and delivering training.
The Gig Economy and Flexible Workforce
Managing a Diverse Workforce: Analyze the impact of the gig economy and the rise of freelancers on HR outsourcing. Discuss how organizations will need to adapt their HR strategies to accommodate a more diverse and flexible workforce.
Talent Marketplaces: Explore the emergence of talent marketplaces and platforms that connect companies with freelance professionals for short-term projects, and how these platforms are changing the way HR operates.
Enhanced Employee Experience
Personalization: Discuss the trend of personalizing the employee experience, including tailored training and benefits packages, to attract and retain top talent.
Employee Wellbeing: Examine how HR outsourcing will increasingly focus on promoting employee wellbeing, from mental health support to wellness programs.
Data Analytics and Predictive HR
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Explore how HR outsourcing providers will leverage data analytics to make more informed decisions about talent acquisition, retention, and overall HR strategy.
Predictive Analytics: Discuss the use of predictive analytics to anticipate workforce trends and identify potential issues before they arise.
Globalization and International HR
Managing a Global Workforce: Analyze the challenges and opportunities of managing a global workforce and how HR outsourcing can assist in navigating international labor laws and cultural differences.
Global Payroll Management: Explore how HR outsourcing will play a crucial role in managing payroll for employees across different countries, ensuring compliance with local regulations.
Ethical and Diversity Considerations
Diversity and Inclusion: Discuss the increasing importance of diversity and inclusion in the workplace and how HR outsourcing will support these initiatives.
Ethical AI: Address the ethical concerns surrounding AI in HR, such as bias in algorithms, and the steps organizations and outsourcing partners must take to ensure fairness.
The Evolving Role of HR Professionals
Strategic HR: Examine how HR professionals will shift from administrative roles to strategic partners within organizations, focusing on long-term talent planning and business growth.
Continuous Learning: Discuss the need for HR professionals to continually upskill to keep pace with technological advancements and changing workforce dynamics.
Preparing for the Future
Summarize the key takeaways from this chapter and emphasize the importance of staying informed about these emerging trends. Encourage organizations to proactively adapt their HR outsourcing strategies to leverage these developments and stay competitive in the ever-evolving world of HR.
With a keen understanding of these future trends, organizations can position themselves as leaders in HR innovation, ensuring that their workforce remains agile, engaged, and well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Sep 26, 2023 | Outsourcing, Outsourcing Techniques
Outsourcing has become an essential component of modern business strategies, allowing companies to focus on their core competencies while leveraging external expertise. However, entering into outsourcing contracts involves numerous legal considerations that can significantly impact the success and sustainability of the outsourcing relationship. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the key legal aspects that businesses must consider when negotiating, drafting, and managing outsourcing contracts.
Defining the Outsourcing Relationship

In the world of business, outsourcing is a strategic decision that can significantly impact an organization’s operations, cost structure, and competitive position. Before diving into the intricacies of legal considerations in outsourcing contracts, it’s essential to establish a strong foundation by clearly defining the outsourcing relationship. This chapter will explore the critical elements of this initial phase.
Defining the Scope of Outsourcing
The scope of outsourcing defines what functions or processes will be transferred to the service provider. Clarity in defining the scope is paramount to avoid misunderstandings later on. Key considerations include:
Core vs. Non-Core Functions: Determine which functions are core to your business and should remain in-house and which non-core functions can be outsourced for efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Scope Creep: Clearly define the boundaries of the outsourcing arrangement to prevent scope creep, where additional responsibilities are added without proper negotiation.
Service Categories: Categorize services into distinct groups, making it easier to manage and evaluate performance.
Identifying Parties and Stakeholders
Identifying the key parties and stakeholders involved in the outsourcing relationship is essential for transparency and accountability. This includes:
Client: The organization outsourcing the services.
Service Provider: The external entity responsible for delivering the outsourced services.
End Users: The individuals or departments within the client organization that will directly interact with the outsourced services.
Third Parties: Any other entities or individuals involved, such as subcontractors or regulatory authorities.
Setting Clear Objectives and Performance Metrics

Setting clear objectives and performance metrics is crucial for measuring the success of the outsourcing relationship. This includes:
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define specific KPIs that reflect the goals and expectations of the outsourcing arrangement. These may include cost savings, quality improvements, or service delivery timelines.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Establish SLAs that outline the expected levels of service, including response times, availability, and quality standards.
Service Quality and Innovation: Consider how the outsourcing partner can contribute to service quality improvements and innovation within the defined scope.
Risk Assessment: Identify potential risks and develop risk mitigation strategies to ensure that the outsourcing arrangement aligns with the organization’s overall risk tolerance.
Exit Strategy: Even before starting the outsourcing relationship, plan for an exit strategy that outlines the process for transitioning services back in-house or to another provider if necessary.
Data Privacy and Security in Outsourcing Contracts
In today’s digital age, data privacy and security have taken center stage in business operations. When entering into outsourcing contracts, organizations must pay meticulous attention to safeguarding sensitive information. This chapter explores the intricate legal considerations surrounding data privacy and security in outsourcing relationships.
Data Protection Laws and Regulations
Understanding and adhering to data protection laws and regulations is paramount when dealing with sensitive data in outsourcing. Key aspects to consider include:
Global Data Privacy Laws: Recognize the applicability of various data protection laws worldwide, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Cross-Border Data Transfers: Address the challenges associated with cross-border data transfers, including ensuring that the service provider complies with international data transfer mechanisms like Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) or Binding Corporate Rules (BCRs).
Data Classification: Categorize data based on sensitivity, ensuring that highly sensitive information receives the highest level of protection.
Data Security Measures
Implementing robust data security measures is a shared responsibility between the client and the service provider. Key considerations include:
Security Protocols: Define security protocols, encryption standards, access controls, and other technical safeguards to protect data from breaches.
Data Encryption: Mandate the encryption of data both in transit and at rest to prevent unauthorized access.
Authentication and Authorization: Establish strict authentication and authorization procedures to limit access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only.
Security Audits and Testing: Require regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities.
Incident Response: Develop a comprehensive incident response plan to address data breaches promptly and minimize potential damage.
Data Breach Response and Notification Requirements
Despite robust security measures, data breaches can occur. Outline the processes for responding to and notifying stakeholders about data breaches:
Breach Identification: Define how breaches will be identified, including monitoring systems and incident reporting.
Notification Requirements: Specify the legal and regulatory requirements for notifying affected individuals, regulatory authorities, and other relevant parties in the event of a breach.
Liability and Remediation: Address liability for data breaches and establish procedures for remediation, including compensation for affected parties.
Audit and Review: Conduct post-breach audits to identify the cause of the breach and implement corrective actions to prevent future incidents.
Subcontracting and Third-Party Compliance
Many outsourcing providers may subcontract certain functions. Ensure that subcontractors also adhere to data privacy and security requirements:
Subcontractor Oversight: Define the client’s right to approve subcontractors and require subcontractors to meet the same data security standards.
Auditing and Monitoring: Establish procedures for auditing subcontractors and monitoring their compliance with data privacy and security obligations.
Liability Chain: Clarify the liability chain in case a subcontractor causes a data breach, ensuring that the client’s interests are protected.
Data privacy and security are paramount in outsourcing contracts due to the potential risks associated with sharing sensitive information. Thoroughly address legal considerations related to data protection, security measures, breach response, and third-party compliance to mitigate risks and ensure a secure outsourcing relationship. In the subsequent chapters, we will explore other crucial legal aspects of outsourcing contracts.
Sep 20, 2023 | Outsourcing, Outsourcing Techniques
Outsourcing has become a valuable strategy for startups looking to scale efficiently and reduce costs. In this chapter, we’ll explore the various advantages of outsourcing, from cost savings to accessing specialized expertise. Learn how outsourcing can help startups focus on core competencies while delegating non-core tasks.
Understanding the Benefits of Outsourcing

Outsourcing has become a cornerstone strategy for businesses of all sizes, including startups, looking to streamline operations and achieve growth. In this chapter, we’ll explore the myriad advantages that outsourcing offers to startups. By understanding these benefits, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions about how outsourcing can propel your startup forward.
Cost Savings
One of the most apparent and immediate advantages of outsourcing is cost savings. Startups often operate on tight budgets, and outsourcing can help reduce operational expenses significantly. By outsourcing non-core functions, such as customer support, data entry, or payroll processing, you can eliminate the need to hire and train in-house staff, invest in office space, and purchase equipment. Outsourcing allows you to pay for services only when you need them, making it a cost-effective choice.
Access to Specialized Expertise
Startups may not have the resources or capacity to hire experts in every domain. Outsourcing enables you to tap into a global pool of specialized talent. Whether you need IT development, digital marketing, graphic design, or legal advice, outsourcing providers often have teams of experts ready to assist. This access to specialized skills can expedite project timelines and improve the quality of work.
Focus on Core Competencies
As a startup founder or entrepreneur, your time and energy are precious. Outsourcing allows you to concentrate on your startup’s core competencies and strategic priorities. By delegating routine and time-consuming tasks to outsourcing partners, you can dedicate more of your resources to innovation, product development, and business strategy.
Scalability and Flexibility
Startups experience fluctuating demands and growth spurts. Outsourcing offers scalability and flexibility that traditional hiring cannot match. You can easily scale up or down your outsourced services to align with your business’s changing needs. This agility ensures that you’re not burdened with excessive overhead during slow periods or understaffed during rapid expansion.
Faster Time-to-Market
In the competitive startup landscape, speed is often critical. Outsourcing can accelerate your time-to-market by leveraging the expertise and resources of experienced outsourcing providers. Whether you’re developing software, launching a new product, or expanding into new markets, outsourcing can help you meet deadlines and gain a competitive edge.
Reduced Risk
Outsourcing can mitigate various risks associated with hiring and managing in-house teams. Employment-related risks, such as turnover, labor law compliance, and benefits administration, are shifted to the outsourcing partner. Additionally, outsourcing can reduce the risk of investing in expensive technology or infrastructure that may quickly become obsolete.
Enhanced Focus on Innovation
By offloading routine tasks and administrative burdens, outsourcing frees up your team to focus on innovation and creativity. Startups that embrace outsourcing often find that their employees are more engaged and motivated when they can devote their energy to strategic initiatives and problem-solving.
Global Reach and 24/7 Operations
Outsourcing can enable your startup to operate on a global scale and provide round-the-clock support to customers. With outsourcing partners in different time zones, you can offer 24/7 customer service, ensuring that your business remains accessible to a worldwide audience.
The Future of Outsourcing for Startups

The landscape of outsourcing is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing global dynamics, and shifting business paradigms. In this chapter, we’ll explore the exciting possibilities and emerging trends that represent the future of outsourcing for startups. By staying ahead of the curve, your startup can harness these developments to gain a competitive edge and drive innovation.
AI and Automation
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and automation is poised to revolutionize outsourcing. Startups can leverage AI-driven chatbots for customer support, automate routine data entry tasks, and use machine learning for data analysis. These technologies not only reduce costs but also enhance efficiency and accuracy, allowing startups to focus on higher-value tasks.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
RPA is gaining traction in outsourcing. It involves using software robots to automate repetitive and rule-based tasks across various departments, from finance to HR. For startups, RPA can lead to significant cost savings, error reduction, and streamlined processes.
Blockchain for Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology is transforming how transactions are conducted in outsourcing contracts. It offers increased transparency, security, and immutability, making it ideal for managing complex supply chains, contracts, and payments. Startups can explore blockchain’s potential to enhance trust and reduce fraud in outsourcing relationships.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are opening new possibilities for training, collaboration, and customer engagement. Startups can outsource AR/VR development to create immersive experiences, virtual training programs, and interactive customer support solutions that set them apart in the market.
Gig Economy Platforms
The gig economy is expanding rapidly, offering startups access to a vast pool of freelance talent. Specialized platforms are emerging to connect startups with freelancers across diverse skill sets, enabling them to tap into expertise without committing to long-term contracts.
Sustainable Outsourcing
Sustainability and corporate social responsibility are gaining prominence. Startups can align their outsourcing practices with sustainable goals, choosing partners who prioritize eco-friendly operations and ethical labor practices. Sustainable outsourcing can enhance brand reputation and attract socially conscious customers.
Edge Computing
Edge computing is becoming essential for businesses requiring real-time data processing and low latency. Startups can outsource edge computing services to ensure their applications and IoT devices operate efficiently, particularly in industries like healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing.
Data Privacy and Security
With increasing concerns about data breaches and privacy violations, startups must prioritize data security in their outsourcing relationships. Emerging regulations and standards are shaping how data is handled globally. Outsourcing partners that adhere to these standards will become more attractive to startups.
Hybrid Workforce Models
The future of outsourcing may involve hybrid workforce models, where startups combine in-house teams with remote workers and outsourcing partners seamlessly. Leveraging technology, startups can create a flexible work environment that optimizes talent and resources.
Ethical AI and Responsible Outsourcing
Startups should consider the ethical implications of outsourcing decisions, especially when AI is involved. Ethical AI principles, such as fairness, transparency, and accountability, should be integrated into outsourcing practices to ensure responsible use of technology.
In conclusion, the future of outsourcing for startups is filled with opportunities to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive innovation. Embracing emerging technologies, sustainable practices, and ethical considerations will be key to navigating this evolving landscape successfully. As a startup, staying adaptable and proactive in adopting these trends will position you for long-term success in the world of outsourcing.
Sep 12, 2023 | Outsourcing, Outsourcing Techniques
In today’s interconnected world, global outsourcing has become a fundamental strategy for businesses looking to remain competitive. While outsourcing offers numerous advantages, such as access to specialized talent and cost savings, it also brings with it the challenge of navigating cross-cultural collaboration. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the importance of cultural intelligence in global outsourcing and provide insights, strategies, and real-world examples to help you successfully navigate the complexities of cross-cultural collaboration.
Understanding Cultural Intelligence
Before delving into the intricacies of cultural intelligence, it’s essential to understand the significance of culture in global outsourcing. Culture encompasses a wide range of factors, including language, customs, values, communication styles, and societal norms. These elements shape how people think, behave, and interact within their cultural contexts.
What Is Cultural Intelligence?
Cultural intelligence, or CQ, refers to an individual’s ability to work effectively in culturally diverse settings. It involves understanding, adapting to, and effectively interacting with people from different cultures. CQ goes beyond basic cultural awareness and requires a deeper level of empathy and competence in cross-cultural situations.
The Importance of Cultural Intelligence in Global Outsourcing

Enhancing Collaboration:
Global outsourcing often involves teams and partners from different countries and cultures. Cultural intelligence is vital for fostering effective collaboration, reducing misunderstandings, and building trust among team members.
Gaining a Competitive Edge:
Companies that invest in cultural intelligence gain a competitive advantage by accessing a broader talent pool and expanding their global reach. Culturally intelligent organizations can better serve diverse customer bases and enter new markets successfully.
Mitigating Risks:
Cultural misunderstandings can lead to costly mistakes, missed opportunities, and damage to a company’s reputation. Cultural intelligence helps mitigate these risks and ensures smoother business operations.
Building Cultural Intelligence
Self-Awareness:
The foundation of cultural intelligence begins with self-awareness. Individuals and organizations must recognize their own cultural biases, values, and assumptions to navigate cross-cultural interactions effectively.
Cultural Learning:
To develop cultural intelligence, continuous learning about different cultures is essential. This includes studying cultural norms, traditions, communication styles, and etiquette.
Empathy and Perspective-Taking:
Empathy is a key component of cultural intelligence. It involves putting oneself in another person’s shoes, understanding their perspective, and showing respect for their cultural values.
Strategies for Successful Cross-Cultural Collaboration
Effective Communication:
Clear and open communication is crucial in cross-cultural collaboration. Strategies such as active listening, avoiding assumptions, and seeking clarification can enhance communication across cultural boundaries.
Cultural Sensitivity Training:
Many organizations provide cultural sensitivity training to their employees. These programs help raise awareness of cultural differences and provide tools for navigating diverse workplace environments.
Building Diverse Teams:
Diverse teams that reflect a range of cultures and backgrounds can bring fresh perspectives and innovative solutions to the table. However, managing diversity effectively requires cultural intelligence.
Challenges and Solutions
Language Barriers:
Language differences can be a significant challenge in global outsourcing. Strategies for overcoming language barriers include using translation tools, offering language training, and utilizing bilingual team members.
Stereotyping and Bias:
Stereotypes and biases can hinder cross-cultural collaboration. Cultural intelligence training helps individuals and teams recognize and overcome these biases, fostering a more inclusive and diverse work environment.
Time Zone and Schedule Conflicts:
Working across different time zones can lead to scheduling conflicts and delays. Companies can address this challenge by adopting flexible work hours and utilizing scheduling tools that accommodate global teams.
Fostering Cultural Intelligence in Organizations
Leadership Commitment:
Cultural intelligence should start at the top. Leaders who prioritize and model cultural intelligence set the tone for the entire organization.
Diversity and Inclusion Initiatives:
Creating a culture of diversity and inclusion is essential. Organizations can establish employee resource groups, mentorship programs, and diversity-focused initiatives to promote cultural intelligence.
Embracing Cultural Intelligence for Global Success
In our increasingly interconnected world, the ability to navigate and thrive in diverse cultural environments is a key determinant of success, especially for businesses engaged in global operations. Cultural intelligence (CQ) has emerged as a crucial skillset for individuals and organizations looking to harness the power of cultural diversity to their advantage. In this article, we will explore the concept of cultural intelligence, its significance in today’s global landscape, and practical ways individuals and businesses can embrace it to achieve global success.
Understanding Cultural Intelligence (CQ)
Cultural intelligence, often abbreviated as CQ, is the capability to function effectively in culturally diverse contexts. It goes beyond simply acknowledging cultural differences; it involves understanding, appreciating, and leveraging these differences for positive outcomes. CQ comprises several key components:
- Cultural Knowledge: Understanding the values, beliefs, practices, and customs of different cultures.
- Cultural Motivation: The willingness and enthusiasm to engage with and adapt to diverse cultural settings.
- Cultural Strategy: The ability to plan and adapt one’s behavior and communication style in cross-cultural interactions.
- Cultural Action: The effective execution of strategies in real-world cross-cultural situations.
The Significance of Cultural Intelligence
Cultural intelligence is more than just a nice-to-have skill; it’s a strategic imperative in today’s globalized business landscape. Here’s why it’s essential:
- Expanding Global Reach
Companies with high CQ can enter new markets with confidence. They understand the cultural nuances that influence consumer behavior and preferences, allowing them to tailor their products and marketing strategies effectively.
- Fostering Innovation
Diverse teams with strong cultural intelligence tend to be more innovative. They bring a variety of perspectives, ideas, and approaches to problem-solving, leading to creative solutions and product enhancements.
- Enhancing Customer Relationships
Cultural intelligence enables businesses to connect with customers on a deeper level. By respecting cultural norms and values, companies can build trust and loyalty, leading to long-lasting customer relationships.
- Effective Cross-Border Collaborations
In global outsourcing, cross-cultural collaboration is the norm. Teams with high CQ can work harmoniously, transcending language and cultural barriers to achieve common goals.
Embracing Cultural Intelligence
- Self-Awareness
The journey toward cultural intelligence starts with self-awareness. Individuals and organizations must recognize their own cultural biases, assumptions, and values. Self-reflection and introspection are essential to this process.
- Education and Training
Cultural intelligence is a skill that can be developed and honed through education and training. Organizations can offer cultural sensitivity training to employees to raise awareness and provide practical tools for navigating cultural differences.
- Cross-Cultural Exposure
Exposure to different cultures through travel, international assignments, or partnerships can significantly boost cultural intelligence. It provides firsthand experience and opportunities to learn from diverse perspectives.
- Empathy and Open-Mindedness
Cultural intelligence requires empathy and open-mindedness. It’s about genuinely trying to understand and appreciate other cultures, even when they differ from one’s own.
Cultural intelligence is not just a soft skill; it’s a critical competency for thriving in today’s interconnected world. Companies that invest in cultural intelligence and embrace cross-cultural collaboration can unlock the full potential of global outsourcing, driving innovation, expanding market reach, and achieving sustainable growth. By understanding, valuing, and adapting to diverse cultures, organizations can navigate the complexities of the global business landscape with confidence and success.
Aug 1, 2023 | Outsourcing, Outsourcing Techniques
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business landscape, agility and flexibility have emerged as crucial factors for staying competitive and adapting to ever-changing market conditions. Companies need to respond swiftly to evolving customer demands, technological advancements, and economic fluctuations to maintain their edge. Outsourcing has emerged as a strategic solution for enhancing business agility and flexibility. By delegating certain tasks and functions to specialized external partners, businesses can focus on their core competencies, respond rapidly to market shifts, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. In this blog post, we will delve into the ways outsourcing can bolster business agility and flexibility, driving success in a rapidly changing world.
Focus on Core Competencies
One of the primary ways outsourcing enhances agility is by enabling businesses to concentrate on their core competencies. Non-core functions, such as IT support, accounting, or customer service, can be outsourced to expert service providers. This shift in focus allows the company’s internal teams to allocate more time and resources to innovation, product development, and strategic decision-making. As a result, the business becomes more nimble and adaptable, ready to capitalize on emerging trends and market demands.
Scalability and Rapid Resource Allocation
Outsourcing provides businesses with a scalable workforce that can be quickly adjusted based on demand fluctuations. During peak seasons or when tackling large projects, additional resources can be seamlessly onboarded from the outsourcing partner. Conversely, during slower periods, businesses can scale down the workforce to optimize costs. This agility in resource allocation enables companies to navigate changing market demands with ease and avoid unnecessary overhead expenses.
Accelerated Time-to-Market
In today’s fast-paced environment, bringing products and services to market quickly is crucial for success. By outsourcing certain tasks, businesses can streamline their development processes and accelerate time-to-market. Remote outsourced teams, often working in different time zones, enable 24/7 operations, allowing companies to maintain continuous progress on projects and significantly reduce development cycles.
Access to Global Talent
Outsourcing opens up access to a vast talent pool across the globe. Businesses are no longer limited to hiring locally; they can collaborate with skilled professionals from diverse backgrounds and expertise. This diversity brings fresh perspectives and innovative solutions to the table, fostering an agile and creative work environment.
Risk Mitigation and Business Continuity
Outsourcing also contributes to business resilience by mitigating risks and ensuring continuity. By diversifying their supply chains and distribution channels through outsourcing, companies can minimize the impact of disruptions. If a disaster strikes in one location, outsourced teams in different regions can continue operations, minimizing downtime and revenue loss.
Rapid Technological Adoption
Keeping up with the latest technological advancements is vital in today’s digital age. Outsourcing partners often invest in cutting-edge technologies and tools to deliver high-quality services. Collaborating with such partners enables businesses to access and implement new technologies quickly, enhancing their own capabilities and staying competitive in the market.
Cost Optimization
Outsourcing offers cost-saving benefits, especially when working with teams in countries with lower labor costs. Companies can allocate resources more efficiently and redirect funds towards strategic initiatives, giving them the financial flexibility to invest in growth opportunities and innovation.
Faster Decision-Making
When non-core functions are outsourced, the decision-making process becomes more streamlined. Internal teams can focus on strategic matters, leading to quicker and more effective decisions. This agility in decision-making is vital for seizing time-sensitive opportunities and responding to market challenges promptly.
Geographic Expansion
Outsourcing can serve as a catalyst for geographical expansion. By working with outsourced teams in different regions, businesses can better understand local markets and adapt their products and services to cater to diverse customer preferences. This enhances their global presence and fosters business resilience by diversifying their customer base.
Common Outsourcing Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Outsourcing can be a powerful strategy for businesses, but it is not without its challenges. Making mistakes in the outsourcing process can lead to inefficiencies, communication breakdowns, and unsatisfactory outcomes. In this blog post, we will explore some common outsourcing mistakes and provide valuable tips on how to avoid them, ensuring a successful outsourcing experience.
Incomplete Due Diligence
Mistake: Rushing into an outsourcing partnership without conducting thorough due diligence on the service provider’s credentials, experience, and reputation can lead to subpar results.
Solution: Take the time to research and evaluate potential outsourcing partners. Review their portfolio, client testimonials, and case studies. Ask for references and verify their expertise before finalizing any agreement.
Focusing Solely on Cost
Mistake: Choosing an outsourcing partner solely based on the lowest cost can result in compromised quality and communication issues.
Solution: Prioritize value over cost. Consider factors like expertise, past performance, and the ability to meet deadlines. Opt for a partner that aligns well with your business goals and can deliver high-quality results within your budget.
Inadequate Communication and Expectation Setting
Mistake: Failing to establish clear communication channels, expectations, and deliverables can lead to misunderstandings and project delays.
Solution: Set up regular communication channels and clearly outline project requirements, deadlines, and key performance indicators (KPIs). Maintain open communication and provide timely feedback to ensure everyone is on the same page.
Neglecting Data Security and Confidentiality
Mistake: Overlooking data security measures and confidentiality agreements can result in data breaches and damage to your business reputation.
Solution: Prioritize data security and establish comprehensive confidentiality agreements with the outsourcing partner. Ensure that they adhere to industry best practices for data protection.
Lack of Proper Contractual Agreements
Mistake: Relying on informal agreements or vague contracts can lead to disputes and legal issues in case of conflicts.
Solution: Draft detailed and well-defined contracts that cover all aspects of the outsourcing arrangement, including deliverables, timelines, payment terms, and dispute resolution mechanisms.
Ignoring Cultural Differences
Mistake: Disregarding cultural differences can hamper effective communication and collaboration between your team and the outsourced team.
Solution: Be culturally sensitive and foster an inclusive work environment. Acknowledge and respect different cultural norms and practices, and promote open dialogue to bridge any communication gaps.
Lack of Flexibility
Mistake: Insisting on rigid terms and processes without allowing room for adjustments can hinder the outsourcing partnership’s success.
Solution: Be open to flexibility and adaptability. Recognize that changes may arise during the project and be willing to discuss and negotiate adjustments to accommodate evolving requirements.
Not Investing in Relationship Building
Mistake: Neglecting to build a strong relationship with the outsourcing partner can lead to a transactional, less productive arrangement.
Solution: Invest time and effort in relationship building. Foster trust, encourage open communication, and treat the outsourcing partner as an extension of your team rather than an external entity.
Lack of Monitoring and Performance Evaluation
Mistake: Failing to monitor the outsourced team’s performance and progress can result in missed deadlines and unsatisfactory deliverables.
Solution: Implement performance tracking and regular evaluations to assess the outsourcing partner’s performance. Address any issues promptly and celebrate successes to reinforce a positive working relationship.
Underestimating Internal Involvement
Mistake: Assuming that outsourcing means minimal involvement from your internal team can lead to misalignment and lack of collaboration.
Solution: Ensure active involvement from your internal team throughout the outsourcing process. Assign dedicated points of contact and provide the necessary support and resources for seamless collaboration.
By being aware of common outsourcing mistakes and taking proactive measures to avoid them, businesses can enjoy the full benefits of outsourcing. Thorough due diligence, effective communication, and strong relationship building are essential components of a successful outsourcing partnership. Remember that outsourcing is a strategic decision, and selecting the right outsourcing partner can lead to increased efficiency, access to specialized skills, and enhanced business performance. With proper planning and a focus on mutual success, businesses can leverage outsourcing as a powerful tool for growth and competitiveness.
Jul 31, 2023 | Outsourcing Techniques
In today’s globalized world, business outsourcing has become a common practice for companies looking to streamline their operations while reducing costs. Business process outsourcing (BPO) involves hiring third-party service providers to handle certain business functions on behalf of a company. While outsourcing can be a great way to improve efficiency and lower expenses, it is important to consider the employee demographic profiles for outsourcing efforts.
Particularly offshore outsourcing operations raise concerns about cultural and language barriers, and may require offshore outsourcing techniques to minimize potential issues. When considering heading offshore outsourcing operations or head offshore outsourcing operations, businesses must weigh the pros and cons of particularly offshore outsourcing efforts. The key is to head outsourcing efforts based on international business research and understanding the particular needs of each outsourcing business venture.
One of the biggest benefits of offshore outsourcing is the cost savings. Offshore outsourcing destinations typically offer lower payroll and overhead costs than domestic outsourcing efforts. However, there are also risks associated with outsourcing business strategies offshore. For example, foreign call center employees may not have the same level of training or experience as domestic ones, which could negatively impact customer service call centers.
Another consideration when it comes to business outsourcing techniques and strategies is the outsourcing call centers’ location. While offshore outsourcing sites may seem like an attractive option for companies looking to cut costs, it is important to take into account the distance and time zone differences that could make communication difficult. It is also important to carefully assess the practices outsourcing techniques of any potential offshore service providers to ensure they meet the company’s standards.
Additionally, sales services may face roadblocks when attempting to reach clients overseas. Cultural differences and language barriers can be difficult hurdles to overcome. Companies must be aware of the offshore outsourcing endeavors they plan to execute and the possible challenges that come with them.
It is important to note that not all business operations moved overseas are successful. Customer dissatisfaction, quality control problems, and other issues can arise when proper due diligence is not taken in the planning process.
Business outsourcing can be a valuable tool for improving efficiency and reducing costs, but it is essential to carefully consider the pros and cons of offshore outsourcing efforts before committing to any outsourcing business venture. Understanding the demographic profiles regarding business outsourcing techniques and strategies can help companies make informed decisions that benefit their bottom line and ensure success in their operations offshore.
Understanding Employee Demographic Profile
Understanding employee demographic profile involves identifying and analyzing the characteristics of a company’s workforce. This includes factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, education level, income, and geographic location. In the context of outsourcing, understanding employee demographic profiles is crucial because it can impact the success of outsourcing efforts.

For instance, when outsourcing business operations to other countries, cultural and language barriers may arise if foreign call center employees lack proper language training or do not understand the cultural nuances of the company’s customer base. Understanding the demographic variables of offshore outsourcing sites can help companies select service providers that have employees with the necessary skills and language capabilities.
Additionally, companies must consider the annual household income of outsourced employees to ensure that they are being paid fairly and in accordance with local labor standards. The cost savings that come from outsourcing should not come at the expense of exploiting cheaper labor teams. By understanding the payroll and overhead costs in various outsourcing destinations, companies can avoid contributing to unfair labor practices.
Moreover, understanding employee demographic profiles can help companies design effective training programs that cater to the needs of their employees. For example, companies could design training programs that take into account the educational background of their employees, making it easier for them to learn and apply the skills required for their jobs. In turn, this can lead to improved service quality and overall productivity.
Employee demographic profile is an essential part of successful outsourcing efforts. It helps companies to identify the right outsourcing strategies and techniques to use while ensuring that they are not contributing to negative global relations or unfair labor practices. By taking employee demographic profiles into consideration, companies can create a more inclusive and effective outsourcing environment that benefits all parties involved.
8 Significant Benefits of Employee Profile

Business process outsourcing has become a popular strategy for companies to reduce costs and improve efficiency. However, to successfully implement outsourcing, it is important to consider the employee demographic profiles for outsourcing efforts. Here are eight benefits of employee profile for business outsourcing:
- Exploit cheaper labor teams: Understanding the demographic variables in various offshore outsourcing sites can help companies to tap into cheaper labor pools, reducing payroll and overhead costs.
- Technical support services: Employee profile can help identify offshore service representatives with the technical expertise required to provide high-quality technical support services.
- Customer support services: By understanding the language capabilities of foreign call center employees, companies can provide better customer support services to their clients.
- Improved service quality: Careful consideration of employee profile can lead to improved service quality when outsourcing is executed properly.
- Strategic outsourcing: Employee profile helps companies to identify which particular business functions to outsource, ensuring that they focus on their core competencies while delegating non-critical operations.
- Reduced outsourcing risks: By carefully selecting offshore service providers, companies can reduce the risks associated with offshore outsourcing.
- Enhanced global relations: Successful offshore outsourcing can help companies establish stronger international trade relations, leading to enhanced global relations.
- Globalized call center setups: Understanding employee profile can help companies to set up globalized call center operations while still maintaining high service quality levels.
Understanding employee profiles is essential when it comes to business outsourcing techniques. By tapping into cheaper labor pools, identifying the right offshore service providers, and focusing on core competencies, companies can achieve their business objectives and improve their departmental operations. When executed properly, offshore outsourcing can lead to significant cost savings, improved service quality, and enhanced global trade relations.










